Heathrow til Lisboa.
I Lisboa bodde vi på hotel Excelsior
Hotellet ligger i en sidegate til den store rundkjøringen
Marquis of Pombal
The Marquis of Pombal Square Portuguese: Praça do Marquês
de Pombal is an important roundabout in the city of Lisbon, Portugal.
It is located between the Avenida da Liberdade (Liberty Avenue)
and the Eduardo VII Park in the former parish of Coração de Jesus
and in the quarter of Santo António.
The square is the radiating point for various important avenues:
Liberdade, Duque de Loulé and Fontes Pereira de Melo, as well as
the streets Braamcamp and Joaquim António de Aguiar.
In the middle of the roundabout there is a large column dedicated to
him, built between 1917 and 1934 and created by Adães Bermudes,
António Couto and Francisco Santos. A bronze statue of the Marquess
is on the top (40 m), with a lion - symbol of power - by his side. The
lower part of the base is surrounded by several allegorical figures,
"namely the female figure symbolizing« re-built Lisbon »and three
sculptural groups evoking the reforms carried out by the Marquess
looking towards the Baixa Pombalina, the area of Lisbon that was
rebuilt under his direction after the disastrous 1755
Lisbon earthquake.
Marquis of Pombal Square - Wikipedia
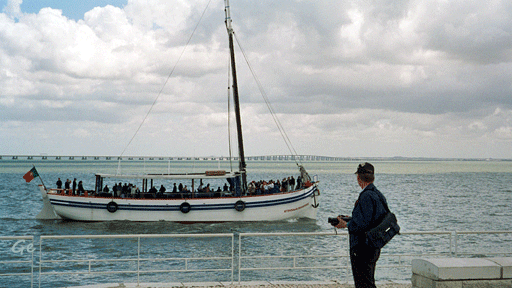
Vi oppholdet i Lisboa med å ta en tur med en
Sightseeing-buss.
1. stopp var på Expo 98

Rundkjøringen Marquis of Pombal
cable-stayed bridge flanked by viaducts that spans the Tagus River in
Parque das Nações in Lisbon, the capital of Portugal.
It is the longest bridge in the European Union, and the second longest
in all of Europe after the Crimean Bridge with a total length of 12.3
kilometres (7.6 mi), including 0.8 kilometres (0.50 mi) for the main
bridge and 11.5 kilometres (7.1 mi) in viaducts. The bridge is served
by 4.8 kilometres (3.0 mi) of dedicated access roads. It was built to
alleviate the congestion on Lisbon's 25 de Abril Bridge, and eliminate
the need for traffic between the country's northern and southern
regions to pass through the capital city.
Construction began in February 1995; the bridge was opened to
traffic on 29 March 1998, just in time for Expo 98, the World's Fair
that celebrated the 500th anniversary of the discovery by Vasco da
Gama of the sea route from Europe to India.
Vasco da Gama Bridge - Wikipedia
Vasco da Gama Bridge
 Vasco da Gama Tower |
The cable car was finished in 1998 and it covers a total distance of 1,2km. At most 8 people can sit in one carrier, but if you want to be only two persons alone, then that is normally possible. Cable car (Telecabine) - Guide to Lisbon The tower was built
in While they were open,
the |
The base of
the building was to be leased for office space after
the
closing of the Expo, but never found tenants. Instead,
it was used
for one-off events, like the world premiere of the new
Mini car in 2001.
Vasco da Gama Tower - Wikipedia
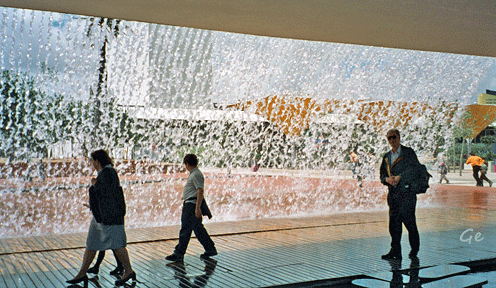
Expo 98

 Santa Justa Lift in Lisbon - Price and operating hours |
The Santa Justa Lift is an
elevator in Lisbon and is the fastest way to
get from the Baixa neighbourhood to the Bairro Alto district. It was inaugurated as one of the city’s public transport systems on 10 July 1902 and was called Elevador do Carmo (Carmo Lift). The Carmo Lift was originally powered by steam until the 6 November 1907, when an electric motor was put in place. |
Fra Expo 98-område gikk til Lisboa sentrum.

Filminnspilling
Mandag 14. mai 2001
En skikkelig regnværsdag med torden og lyn.
Vi gikk først opp til Castelo de Sao Jaorge
São Jorge Castle (Castelo de São Jorge) is one of Lisbon’s most
emblematic landmarks. The silhouette of the Castle stands out
both by day and when illuminated at night, located on the
summit of São Jorge hill, the highest in Lisbon. The hillside also
houses two of the city’s neighbourhoods called Alfama and
Castelo.
A small fortress was built by the Visigoths during the fifth century.
It was modified and enlarged by the Moors in the mid-eleventh
century and during the reign of Afonso I of Portugal (1109 – 1185),
it was altered and in later years transformed into a Royal Palace.
Finally, it was completely restored in 1938.
The Castle reached its maximum splendour during the thirteenth
century and lasted until the sixteenth century when it was
occupied by both the Kings of Portugal and the Bishop.
São Jorge Castle - Hours, prices and how to get there - Lisbon
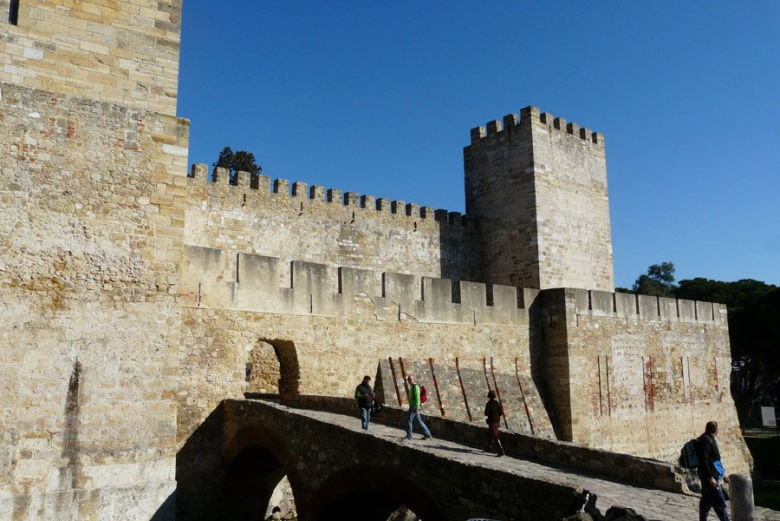

São Jorge Castle (Castelo de São Jorge)
São Jorge Castle - Hours, prices and how to get there - Lisbon

Så tok vi en rundtur med trikken
way of getting around the Portuguese capital. Going fully
electric in 1902, the Rede de eléctricos de Lisboa had 27 lines at
its peak in 1959, before later going into a decline.
Now, the six existing lines are set to grow once more.
Originally entering service in 1873, Lisbon’s tram network once
covered the whole breadth of the city. Today, however, only the
southern and western areas of Lisbon have an operational tram
system, and the rest of the city is connected by a range of bus
and metro routes.
Still, the unique aesthetic of Lisbon’s trams draws tourists, who
keep hopping on board. The classic yellow carriages, known as
remodelados, have become a universally recognised symbol of
Lisbon, widely photographed and shared on social media.
Trams in general are known locally as eléctricos.
A Complete Guide to the Picturesque Trams of Lisbon (theculturetrip.com)
Vi tok toget ut fra byen til Belem.

Stasjonen i Belem

Belém Tower (Portuguese: Torre de Belém, officially the
Tower of Saint Vincent (Portuguese: Torre de São Vicente)
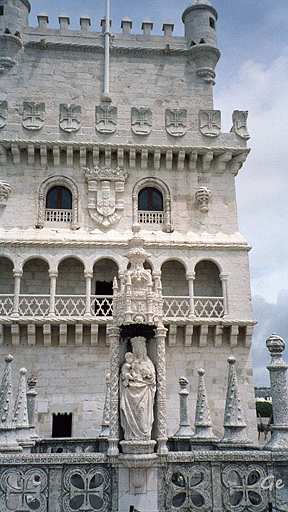 |
Torre de Belem, Torre de São Vicente) is a 16th-century fortification located in Lisbon that served as a point of embarkation and disembarkation for Portuguese explorers and as a ceremonial gateway to Lisbon. It was built during the height of the Portuguese Renaissance, and is a prominent example of the Portuguese Manueline style, but it also incorporates hints of other architectural styles. The structure was built from lioz limestone and is composed of a bastion and a 30-metre (98.4 ft), four-storey tower. Belém Tower - Wikipedia |

Karl Martin er på Torre de Belem.
Broa er Ponte 25 de Abril, og elva er Tajo
.
Portuguese: Ponte 25 de Abril, 25th of April Bridge is a suspension bridge connecting the city of Lisbon, capital of Portugal, to themunicipality of Almada on the left (south) bank of the Tagus river.
It was inaugurated on August 6, 1966. It is often compared to the
Golden Gate Bridge in San Francisco, because they are both suspension
bridges of similar color.
It was built by the American Bridge Company which constructed the
San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge but not the Golden Gate. With a total
length of 2,277 metres (7,470 ft), it is the 40th largest suspension bridge
in the world and the largest bridge in Europe.
The upper deck carries six car lanes while the lower deck carries a double
track railway, electrified at 25 kV AC. The lower deck was added in 1999.
25 de Abril Bridge - Wikipedia

Fra Torre de Belem
Tagus River, Portuguese Rio Tejo, Spanish Río Tajo, longest
waterway of the Iberian Peninsula. It rises in the Sierra de
Albarracín of eastern Spain, at a point about 90 miles (150 km)
from the Mediterranean coast, and flows westward across
Spain and Portugal for 626 miles (1,007 km) to empty into the
Atlantic Ocean near Lisbon. Its drainage basin of 31,505 square
miles (81,600 square km) is only exceeded on the peninsula by
that of the Ebro River, to the northeast. The Tagus covers the
heart of Portugal and Spain and has been of vital importance to
the modern economic development of the two nations.
Tagus River | river, Iberian Peninsula | Britannica
| Kart
på Sjøfartsmuseet i Belem |
 |

The Jerónimos Monastery
place, which was dedicated to Santa Maria de Belém and where the monks of
the military-religious Order of Christ provided assistance to seafarers in
transit.
The harbour of Praia do Restelo was an advantageous spot for mariners, with
a safe anchorage and protection from the winds, sought after by ships entering
the mouth of the Tagus.
The existing structure was inaugurated on the orders of Manuel I (1469–1521)
at the courts of Montemor o Velho in 1495, as a final resting-place for
members of the House of Aviz, in his belief that an Iberian dynastic kingdom
would rule after his death. In 1496, King Manuel petitioned the Holy See for permission to construct a monastery at the site. The Hermitage of Restelo
(Ermida do Restelo), as the church was known, was already in disrepair when Vasco da Gama and his men spent the night in prayer there before
departing on their expedition to the Orient in 1497 .
Moore about the Monastery: Jerónimos Monastery - Wikipedia
European Portuguese: c. 1460s – 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and the first European to reach India by sea.
His initial voyage to India (1497–1499) was the first to link Europe and
Asia by an ocean route, connecting the Atlantic and the Indian oceans
and therefore, the West and the Orient.
This is widely considered a milestone in world history, as it marked the beginning of a sea-based phase of global multiculturalism. Da Gama's
discovery of the sea route to India opened the way for an age of global imperialism and enabled the Portuguese to establish a long-lasting colonial empire in Asia.
The violence and hostage taking employed by da Gama and those who
followed also assigned a brutal reputation to the Portuguese among
India's indigenous kingdoms that would set the pattern for western colonialism in the Age of Exploration.
Traveling the ocean route allowed the Portuguese to avoid sailing
across the highly disputed Mediterranean and traversing the dangerous Arabian Peninsula.
The sum of the distances covered in the outward and return voyages
made this expedition the longest ocean voyage ever made until then,
far longer than a full voyage around the world by way of the Equator
Vasco da Gama - Wikipedia
most notable monuments of Lisbon and Portugal alike, such as the
Belém Tower, the Jerónimos Monastery, the Padrão dos
Descobrimentos, and Belém Palace (official residence of the P
resident of Portugal). The population in 2011 was 16,528.
With the establishment of the Kingdom of Portugal by Afonso III, royal
surveys, or inquirições gerais (general inquiries), were made at his
command to inspect titles of lands claimed by the nobility and clergy,
determined that the population around Lisbon was dispersed
throughout the lowlands, which were suitable for agriculture.
Consequently, Belém was connected to the neighbouring city by
a bridge at Alcântara. Belém's proximity to the River Tagus also
encouraged the development of commercial activities in the small
village of Aldeia do Restelo, which attracted mariners and other
seafarers seeking safe anchorage and protection from the winds
when they entered the river.
In the 14th century, Moors settled on and cultivated the
surrounding lands, providing the city with produce; other Moors,
both free and enslaved, worked in the fishing industry. Meanwhile,
settlement in Restelo grew slowly towards Lisbon.
Belém (Lisbon) - Wikipedia
The Padrão dos Descobrimentos (Monument to the Discoveries)
stands 170 Ft (52 m) tall. This stunning monument was designed to commemorate the Age of Discoveries in Portugal. It was
inaugurated in 1960, on the fifth centenary of one of the
country’s great discoverers, Prince Henry the Navigator, who
discovered the Azores, Madeira and Cape Verde.
The tribute is located on the coast of Belém, near Lisbon and is
also very close to other important sights like Belém Tower and
Jerónimos Monastery.
The Monument to the Discoveries is made up of a group of
sculptures that represent the prow of a caravel (a small sailing
ship constructed by the Portuguese to explore the Atlantic Ocean).
Leading the ship is Prince Henry the Navigator and behind him
are many other great Portuguese discoverers.
Monument to the Discoveries in Lisbon - Padrão dos Descobrimentos
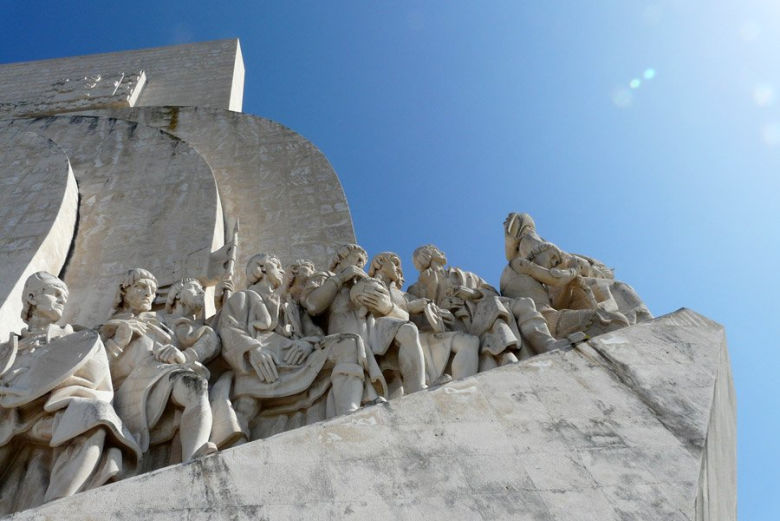

Monument to the Discoveries in Lisbon - Padrão dos Descobrimentos

Vi begynte dagen med en trikketur til
Geologisk museum og Botanisk Hage
Etterpå gikk vi litt rundt i byen.
Vi så blant annet Águas Livres Aqueduct

bilde fra: Águas Livres Aqueduct - Wikipedia
Vi var også på kjøpesenteret Amoreiras
Vi tok tog til Sintra.
19th-century Romanticist architecture, historicestates and villas,
gardens, and royal palaces and castles, which resulted in the
classification of the town as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Sintra's landmarks include the mediaeval Castle of the Moors,
the romanticist Pena National Palace and the Portuguese
Renaissance Sintra National Palace.
Sintra - Wikipedia

Deretter gikk vi til Palacio-Nacional
The Palace of Sintra (Portuguese: Palácio Nacional de Sintra), also
called Town Palace (Palácio da Vila), is located in the town of Sintra,
in the Lisbon District of Portugal. It is a present-day historic house
museum.
It is the best-preserved medieval royal residence in Portugal, being
inhabited more or less continuously from at least the early 15th
century to the late 19th century. It is a significant tourist attraction,
and is part of the cultural landscape of Sintra, a designated
UNESCO World Heritage site.
Much of the palace dates from the times of King John I, who sponsored
a major building campaign starting around 1415.
Most buildings around the central courtyard - called the Ala Joanina
(John's Wing) - date from this campaign, including the main building
of the façade with the entrance arches and the mullioned windows in Manueline and Moorish styles called biforas, the conical chimneys
of the kitchen that dominate the skyline of the city, and many rooms.
Sintra National Palace - Wikipedia

Fra Sintra ser vi opp mit en borg fra 800-tallet
og et slott fra 1800-tallet.
The Moorish Castle was founded under Islamic rule, occupied a then
strategic position for defending both the surrounding territory and
the maritime access routes to the city of Lisbon.
The artefacts found on this site identify how, in between the walls and
their adjoining areas, there lived a population in an area now named
the Islamic Quarter.
The Moors lived here through to 1147, when Sintra was handed over to
Afonso Henriques, the first King of Portugal, following the conquest of
the cities of Lisbon and Santarém,
The History of the Moorish Castle - Sintra (parquesdesintra.pt)

Isolated on its lofty perch, one of the peaks in the Sintra Hills, the
Moorish Castle is a fortification founded in the 10th century during
the period the Moors occupied the Iberian Peninsula.
Its famous walls snake across the hills with their granite blocks
interlinking boulders and cliffs.
the Palace of Pena and, further in the distance, the greens of these
hills contrast with the blues of the Atlantic Ocean.
Moorish Castle - Sintra (parquesdesintra.pt)

Fra borgen ser vi opp Palácio da Pena på toppen av høyden.
The palace is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the
Seven Wonders of Portugal.
It is also used for state occasions by the President of the
Portuguese Republic and other government officials.
Pena Palace - Wikipedia
| The Pena
Palace (Portuguese: Palácio da Pena) The castle's history started in the Middle Ages when a chapel dedicated to Our Lady of Pena was built on the top of the hill above Sintra. According to tradition, construction occurred after an apparition of the Virgin Mary. |
 Det går buss opp til slottet, men valgte å gå opp. |
In the 18th century the monastery was severely damaged by lightning.
However, it was the Great Lisbon Earthquake of 1755, occurring shortly
afterwards, that took the heaviest toll on the monastery, reducing it to ruins. Nonetheless, the chapel (and its works of marble and alabaster attributed to Nicolau Chanterene) escaped without significant damage.
For many decades the ruins remained untouched, but they still astonished young prince Ferdinand. In 1838, as King consort Ferdinand II, he decided to acquire the old monastery, all of the surrounding lands, the nearby Castle of
the Moors and a few other estates in the area. King Ferdinand then set out to transform the remains of the monastery into a palace that would serve as a
summer residence for the Portuguese royal family.
Pena Palace - Wikipedia
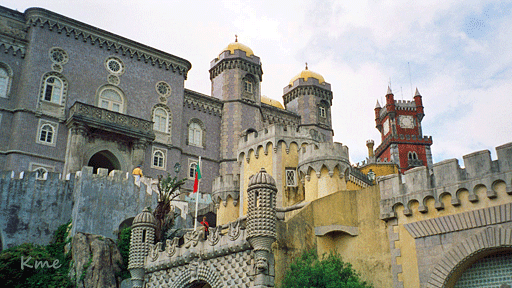
Palácio da Pena

Sintra
Siste hele dag i Portugal.
Vi reiste ut til Cascais og Estoril

Stranda i Cascais/Estoril.
Flott strand, men litt kaldt i vannet så tidlig på året.

Cascais's history as a popular seaside resort originated in the 1870s,
when King Luís I of Portugal and the Portuguese royal family made
the seaside town their residence every September, thus also
attracting members of the Portuguese nobility, who established a
summer community there.
Cascais is known for the many members of royalty who have lived
there, including King Edward VIII of the United Kingdom, King
Juan Carlos I of Spain, and King Umberto II of Italy. Exiled Cuban president Fulgencio Batista was also once a resident of the
municipality. The Casino Estoril inspired Ian Fleming's first James Bond novel Casino Royale.
The municipality is one of the wealthiest in both Portugal and the
Iberian Peninsula. It has one of the most expensive real estate
markets and one of the highest costs of living in the country and
is consistently ranked highly for its quality of life.
Cascais - Wikipedia
Estoril
The territory of Estoril has been inhabited for centuries, owing to its
climatic conditions and favourable environment. Throughout the civil
parish there are scattered remains of these early
communities — Phoenicians, Romans and Arabs selected this area
for its strategic place in Western Europe. There are remains of Roman
villas in the parish that push back the history of the region to the first
millennium, when the settlements of the coast were dependent on the
fishing ports. From these settlements, Estoril inherited a rich cultural
heritage, architecture, toponymy, habits and customs.
Estoril - Wikipedia
Lisbon; Portuguese: Lisboa, is the capital and the largest city of
Portugal, with an estimated population of 505,526 within its
administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Lisbon's urban area
extends beyond the city's administrative limits with a population
of around 2.8 million people, being the 10th-most populous urban
area in the European Union.
About 3 million people live in the Lisbon metropolitan area, which
represents approximately 27% of the country's population. It is mainland Europe's westernmost capital city and the only one
along the Atlantic coast.
Lisbon lies in the western Iberian Peninsula on the Atlantic Ocean
and the River Tagus. The westernmost portions of its metro area, the Portuguese Riviera, form the westernmost point of Continental
Europe, culminating at Cabo da Roca.
Lisbon is one of the oldest cities in the world, and the second-oldest
European capital city (after Athens), predating other modern
European capitals by centuries. Julius Caesar made it a municipium
called Felicitas Julia, adding to the name Olissipo. Ruled by a series of Germanic tribes from the 5th century, it was captured by the
Moors in the 8th century. In 1147, the Crusaders under Afonso Henriques reconquered the city and since then it has been the
political, economic and cultural center of Portugal.
Lisbon - Wikipedia
Portugal officially the Portuguese Republic (Portuguese:
República Portuguesa , is a country located on the Iberian
Peninsula, in southwestern Europe. It is the westernmost sovereign
state in mainland Europe, being bordered to the west and south by
the Atlantic Ocean and to the north and east by Spain. Its territory
also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira,
both autonomous regions with their own regional governments.
The official and national language is Portuguese.
Portugal is the oldest nation state on the Iberian Peninsula and one
of the oldest in Europe, its territory having been continuously settled,
invaded and fought over since prehistoric times. It was inhabited by
pre-Celtic and Celtic peoples, visited by Phoenicians-Carthaginians,
Ancient Greeks and ruled by the Romans, who were followed by the
invasions of the Suebi and Visigothic Germanic peoples.
After the Muslim conquest of the Iberian Peninsula, most of its territory
was part of Al-Andalus. Portugal as a country was established during
the early Christian Reconquista. Founded in 868, the County of
Portugal gained prominence after the Battle of São Mamede (1128).
The Kingdom of Portugal was later proclaimed following the Battle
of Ourique (1139), and independence from León was recognized by
the Treaty of Zamora (1143).
In the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal established the first global
maritime and commercial empire, becoming one of the world's major
economic, political and military powers. During this period, today
referred to as the Age of Discovery, Portuguese explorers pioneered
maritime exploration with the discovery of what would become
Brazil (1500). During this time Portugal monopolized the spice trade,
divided the world into hemispheres of dominion with Castile,
and the empire expanded with military campaigns in Asia. However,
events such as the 1755 Lisbon earthquake, the country's occupation
during the Napoleonic Wars, and the independence of Brazil (1822)
erased to a great extent Portugal's prior opulence
Portugal - Wikipedia
